Part:BBa_K2981004
TyrR, a DNA binding protein, controls the biosynthesis of Phe and Tyr in E. coli
The biosynthesis of Phe and Tyr in E. coli is controlled by the DNA binding protein TyrR. The TyrR protein binds to the consensus DNA sequence TGTAAAN6TTTACA (referred to as the TyrR box), which is classified as strong or weak. In the presence of Phe, binding of the TyrR dimer to the strong cassette in vitro strongly induces gene expression by promoting binding of the RNA polymerase to the promoter or promoting binding of the second dimer to the adjacent weak box. In the presence of Tyr and ATP, the TyrR dimer self-associates to form a hexamer, and the hexamer binds weakly to the weak consensus of the consensus sequence, due to weak-frame-bound RNA polymerase forming an open complex or leaving the initiation Impaired ability of the child leads to inhibition of gene expression. Thereby regulating the repression of aroF, tyrP.
Characterization by AFCM-Egypt team 2022
AFCM-Egypt team 2022 characterized this part through: literature characterization, characterization of mutational landscape, and characterization by mathematical modeling in this part BBa_K4140001
Literature Characterization by AFCM-Egypt team 2022
ATPase activity of tyrR:
In this study, TyrR has poor ATPase activity that ranges between 12 and 400 mmol of ATP mol−1 monomer min−1. TyrR-(188–467) posess a specific ATPase activity of 105 mmol of ATP mol−1 monomer min−1, about five times the value for TyrR, which was found in this study to be 20 mmol of ATP mol−1 monomer min−1. As shown in figure 1, the flow dialysis demonstrates that TyrR binds to ATP with a half saturation value of 3.1 m. TyrR-(188-467) binds to ATP with a half saturation value of 7.6 m. TyrR-(188-467) had a 1.4 m dissociation constant when it coupled to rhodamine-ATP. These findings demonstrate that TyrR-(188-467) had a 2- to 5-fold reduced affinity for binding ATP and rhodamine-ATP than TyrR.
Dixon, M. P., Pau, R. N., Howlett, G. J., Dunstan, D. E., Sawyer, W. H., & Davidson, B. E. (2002). The central domain of Escherichia coli TyrR is responsible for hexamerization associated with tyrosine-mediated repression of gene expression. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 277(26), 23186-23192.
Characterization of Mutational Landscape by AFCM-Egypt team 2022
After creating a multiple sequence alignment of the protein sequence and predicting mutational landscapes, the effect of these mutations on the evolutionary fitness of the protein is tested. The prediction of the mutational landscape by saturation mutagenesis of the TyrR protein. The (C374R) mutation, as depicted in the chart, had the greatest score when compared to other mutations. On the other hand, it's clear that the (K399Q) had the least evolutionary fitness for TyrR protein. As displayed in Figure(3)
Characterization by mathematical modeling by AFCM-Egypt team 2022
We are using mathematical modeling to detect the increased level of phenylalanine (phe) in phenylketonuria patients in our diagnostic platform. It depends on a whole cell-based biosensor through a cascade of reactions to finally end by formation of β-galactosidase that turns the color into blue once bound to its substrate (X-gal) as mentioned in figure (4) and graph (1).
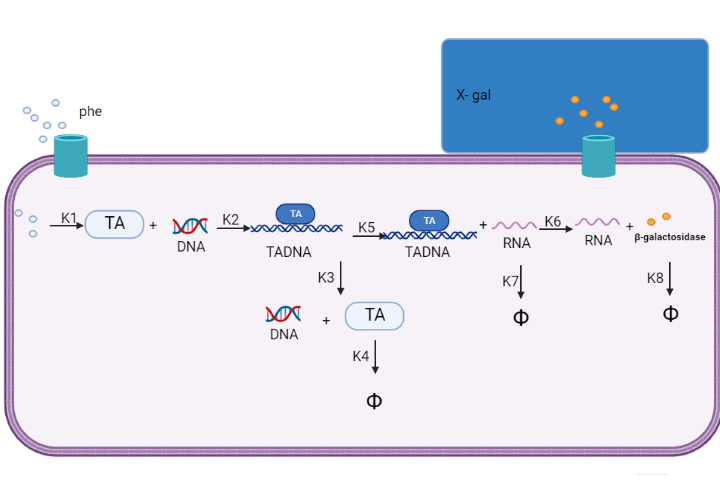
Figure (4) represents the cascade of reactions in whole cell-based biosensor model.
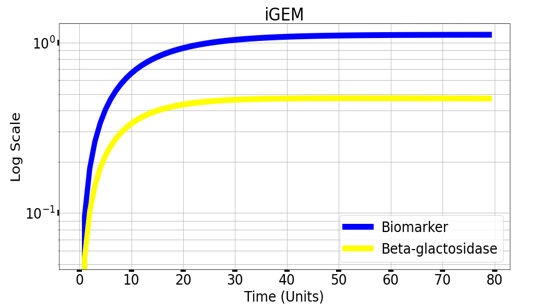
Graph(1) illustrates a direct relation between biomarker and beta-galactosidase ,so as the biomarker increases, the released amount of beta-galactosidase increases till it reaches constant value after about 30 time units. Therefore, the maximum amount of the biomarker releases the maximum amount of beta-galactosidase.
Experimental Characterization by AFCM-Egypt 2022
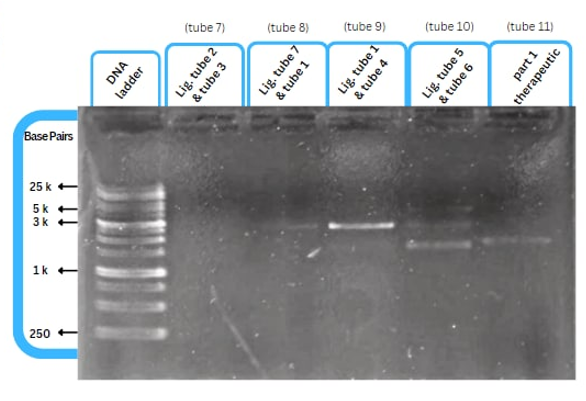
This figure shows an experimental characterization of this part as it's validated through gel electrophoresis as it is in lane 6 (the last one). The run part (ordered from IDT) included T7P - TyrR RBS - TyrR - TyrPromoter.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal BglII site found at 720
Illegal BglII site found at 1062 - 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal AgeI site found at 526
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
| None |